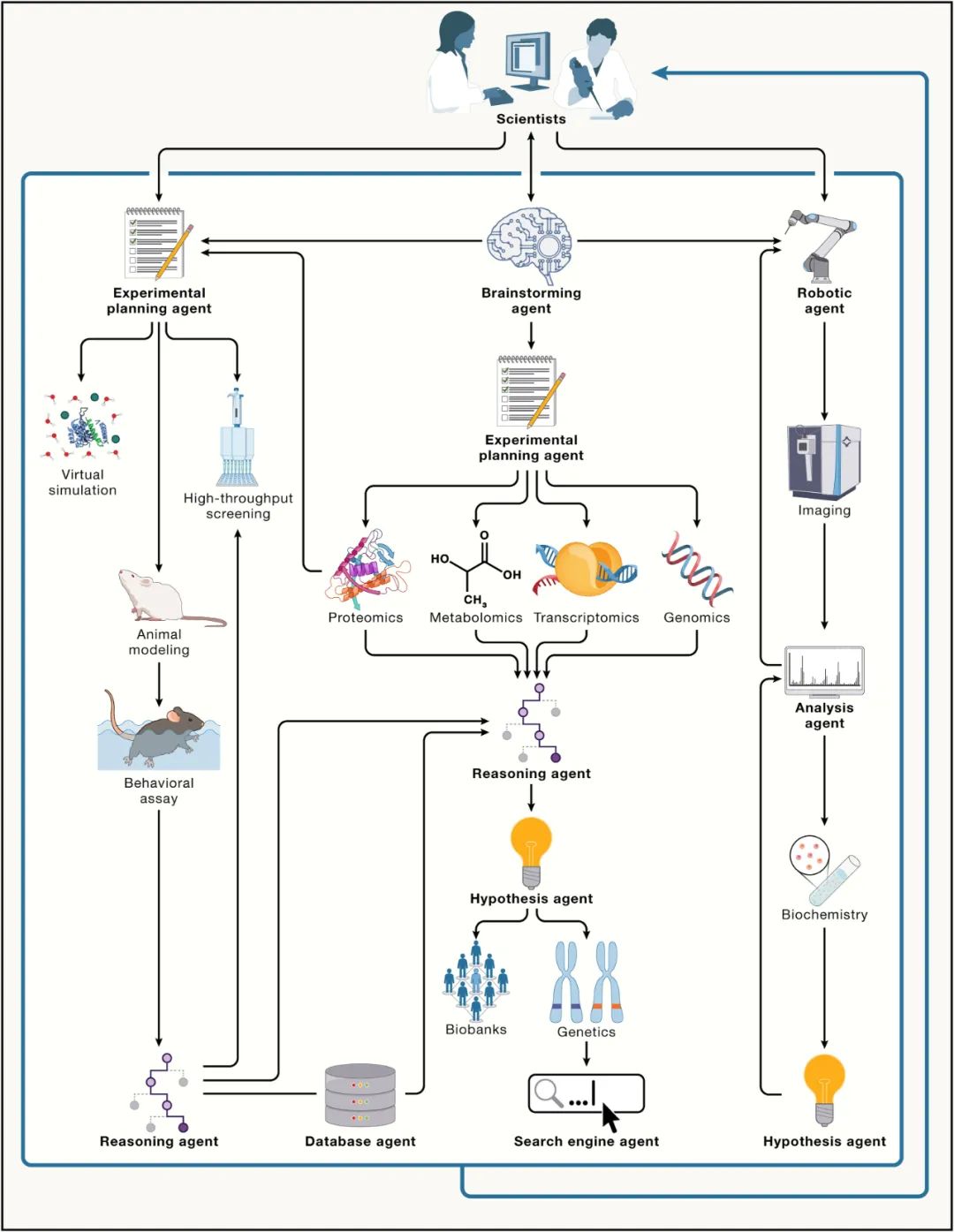
It is difficult to expand the production of mask "heart" melt-blown nonwoven fabric with a unit price of 20 thousand to 300 thousand

In the workshop of Shandong Junfu Nonwoven Fabric Co., Ltd., workers are processing non-woven fabrics for masks. (Tonglian photo, provided by the interviewed enterprises)
From the usual 20 thousand yuan/ton, it has risen to more than 300 thousand yuan/ton, and the industry expects it to rise in the future … … Melt-blown non-woven fabrics (hereinafter referred to as melt-blown fabrics), known as the "heart" of masks, have increased their prices by more than 15 times in recent months, forming a very strong seller’s market.
During the epidemic period, masks are important protective equipment, and they have become a must-have for first-line medical care, enterprises returning to work, and people traveling, and the market demand has soared. The new production capacity of masks in China has doubled rapidly, and the supply of melt-blown cloth, the core raw material, is in short supply.
How scarce are the core raw materials of masks? What is the root cause of the skyrocketing price of meltblown fabrics? A large number of mask production lines have been put into production. Why don’t manufacturers take the opportunity to expand the production capacity of meltblown fabrics? When can we alleviate the shortage of raw materials for masks? With relevant questions, the reporter tracked the upstream industrial chain of masks and investigated key production links such as mask factories, cloth factories and material factories.
Tight cloth
Melt-blown fabrics are in short supply and their prices are rising rapidly, forming a very strong seller’s market.
"Everything is easy to say except meltblown cloth." In a mask supply sharing exchange group, a manufacturer said this.
The group brings together more than 100 related manufacturers in the upstream and downstream of the mask industry, and they will exchange information related to masks in the group. Although the prices of materials such as ear straps and nose bridge strips are also rising, the supply is not in short supply. Only meltblown cloth forms a very strong seller’s market.
"Recently, the inquiry for meltblown fabrics has quoted at least 200,000 yuan/ton, and it is not unusual for 300,000 to 400,000 yuan. Two weeks ago, we purchased 80,000 yuan/ton, and the highest was 120,000 yuan/ton. " Recently, a Shandong clothing company that switched to masks and other epidemic prevention materials "has no way to find materials". Ding Yan, the person in charge of the company, said that the rapid rise in the price of meltblown fabrics made people unprepared.
Melt-blown cloth is the key material to filter viruses for masks, and it can be called the "heart" of medical surgical masks and N95 masks. Medical surgical masks generally adopt multi-layer structure, which is called SMS structure for short: single-layer spunbonded layer (S) on the inside and outside, and single-layer or multi-layer meltblown layer (M) in the middle, and meltblown cloth is the best material for the meltblown layer.
Without meltblown cloth, we can only "let the machine wait for the cloth" Qingdao Hainuo Bioengineering Co., Ltd. owns two production lines of medical surgical masks and one production line of civil masks. They once reported to the local government that some production lines had to stop production because of the shortage of raw materials and the unavailability of goods.
"Meltblown fabrics that meet medical standards can’t be bought now," said the person in charge of Sheng Da Medical Hygiene Materials Co., Ltd., whose inventory of meltblown fabrics can only be used until the beginning of March. The company now has a mask production line, and two new lines will arrive at the factory in early March, when the daily demand for meltblown fabrics will increase from the current 80 to 90 kilograms to about 200 kilograms. If meltblown fabrics can’t be purchased, the new lines will be difficult to put into production. At present, the company has reported the demand information to government departments, hoping to solve the problem of medical meltblown cloth gap in the near future.
A flood of demand
On the demand side of melt-blown fabrics, the number of masks has increased greatly, and some manufacturers are looking for materials everywhere to raise the price of fabrics.
According to the introduction of the National Development and Reform Commission, the current capacity utilization rate of masks in China has reached 110%. As of February 29th, the daily capacity of masks in China has reached 110 million, and the daily output has reached 116 million. At present, 30 provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities except Tibet have successively set up new mask production lines, and at the same time, new mask production lines will be put into production. The person in charge of China Textile Business Association said that in the future, the market demand for meltblown fabrics will further increase.
In order to alleviate the shortage of masks, it has become an important way for non-mask manufacturers to become mask manufacturers. At present, many governments have opened up green channels to speed up examination and approval, and encouraged enterprises related to the industrial chain to switch to emergency production. Based on industrial and commercial registration’s changed information, from January 1st to February 7th, more than 3,000 enterprises in China added "masks, protective clothing, disinfectant, thermometers and medical devices" to their business scope.
In the "Docking Zone for Production Process of Key Medical Prevention and Control Materials" launched by the State Council Client applet on February 21st, the reporter saw that most enterprises are seeking the supply of meltblown cloth.
The reporter found that the recent surge in cloth prices was mainly reflected by small and medium-sized mask factories and new mask factories that had just changed production. The relevant person in charge of the Shandong Provincial Department of Industry and Information Technology said that the price of masks is high, and the production of masks is profitable. Coupled with the initiative of local governments, many enterprises have switched to masks, and the demand for raw materials has increased greatly, and the supply is not enough.
In order to ensure the supply of epidemic prevention materials in the first line of medical care, the national and local industry and information departments have formulated a number of key enterprises to ensure materials. The production of these mask factories and cloth factories is monitored by the government, and the sales are dispatched by the government, and the price increase is relatively controllable. However, people in the industry believe that there are a large number of mask factories that have emerged recently, and there are no stable suppliers. They can only look for raw materials everywhere, and they will not hesitate to buy materials.
A restless supply of goods
At the supply end of meltblown cloth, there are small factories sitting on the ground, and at the circulation end of meltblown cloth, there are middlemen who take the opportunity to earn the difference.
Walking into the factory of Shandong Junfu Nonwoven Fabric Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Shandong Junfu) located in Dongying City, Shandong Province, the reporter saw a busy scene. It is reported that they have been working overtime since receiving the notice from the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology on January 27, and all 10 production lines are producing at full capacity 24 hours a day. The daily output of meltblown cloth produced by Shandong Junfu is about 13 tons, accounting for 1/10 of the whole country. According to the scheduling of the state and relevant departments, it is mainly supplied to downstream enterprises in Hubei and Shandong.
There are not many large-scale manufacturers that can produce meltblown fabrics in China. The industry has been lacking attention for a long time, showing a tepid situation, and the industry as a whole has shown a small and scattered situation. At present, the domestic meltblown cloth production capacity is mainly distributed in a few provinces and cities such as Shandong, Guangdong, Zhejiang and Jiangsu.
At the supply end of meltblown cloth, the price increase of large cloth factories is not large under the control of the government, but some small factories sit on the ground and start at the price.
"The usual price of meltblown cloth is about 20,000 yuan/ton, and now our price is 100,000 yuan/ton. Because of our price reduction, local small cloth factories dare not raise prices, but in some provinces and regions lacking leading enterprises, small cloth factories raise prices for each other, and the prices are all above 200,000 yuan/ton. Many small mask factories want to use our materials and ask the local government to coordinate. I receive two or three hundred calls a day. " Huang Wensheng, general manager of Shandong Junfu, said.
A person in charge of a mask factory in Xiantao, Hubei Province said that at present, the local price of meltblown cloth in Xiantao is about 200,000 yuan/ton, while the price before the epidemic was about 22,000 yuan/ton; According to the manufacturer of meltblown cloth in Nantong, Jiangsu, in order to make the mask production line run normally, some mask factories offered high prices to buy meltblown cloth.
Many small cloth factories that are not included in the supply list of mask raw materials have raised prices seriously. Lin Youqiang, the person in charge of a mask manufacturer in Shandong, said that meltblown cloth enterprises with stable customers at ordinary times should not raise prices arbitrarily to maintain customer relations; A group of enterprises with no stable partners and poor management in the past maliciously raised their prices, hoping to make a quick sum of money.
According to industry insiders, some meltblown cloth suppliers are quite "strong" in the market, not only issuing less or no invoices for delivery, but also requiring downstream factories to use "hard currency" masks to offset the payment at a discount, and to add cash.
At the circulation end of meltblown cloth, there are middlemen who take the opportunity to earn the difference.
A small and medium-sized enterprise owner who switched to production of masks told reporters that in some WeChat groups where mask raw material resources are connected, middlemen arbitrarily charge high prices. "They opened their mouths and offered a high price of 300,000 to 300,000 yuan per ton, taking advantage of our lack of goods to rush production, and often said ‘ If necessary, transfer the money quickly. You don’t want people to get the goods ’ , create ‘ Seconds rise and kill ’ The tension. "
The relevant person in charge of the Industrial and Information Bureau of a city in Shandong Province said that many people hoard goods and sell them upside down, and the price is greatly increased. Many meltblown fabrics stay in the warehouse and circulation, waiting for the price increase, and supply and demand cannot match well.
A handsome profit
The reporter learned that the amazing profit of masks is an important reason why mask factories are willing to buy meltblown fabrics at high prices.
An insider calculated a cost account for the reporter: 1 ton of meltblown cloth can make 1 million medical surgical masks. If the meltblown fabric sells for 200,000/ton, the fabric price only accounts for 0.2 yuan in the cost of a mask. At present, the price of masks allocated by the government from Shandong is about 1.5 yuan each, and 0.2 yuan is subsidized; Each of Beijing is about 4 yuan, and each of Shanghai and Hubei is about 3 yuan. Although the cost of logistics, labor and melt-blown polypropylene has doubled recently, it also accounts for a small proportion in the price of masks.
On the other hand, the demand for masks has increased greatly, and some enterprises anxious to return to work do not care about the price of raw materials, which has pushed up the price of masks. "Recently, there has been a wave of enterprises returning to work all over the country. The state requires enterprises to distribute protective equipment such as masks for their employees. If each employee of each enterprise uses a mask a day, this is an astronomical figure." Lin Youqiang said.
According to the data of the fourth national economic census, the total employment population of domestic legal entities and self-employed households is as high as 533 million, and at least 533 million masks are needed every day based on one mask per person per day. Compared with the current daily production capacity, the mask gap is huge, and the profit margin can be imagined.
Awkward "thin waist"
The production capacity of enterprises related to the mask industry chain is "gourd-shaped", which is one of the root causes of the shortage of meltblown cloth.
Yu Xiaoning, chairman of Shandong Daoen Group, said that the downstream mask factory is growing rapidly at present, and the national production capacity has increased by about 2 times in the last month, which is the "bottom of the gourd"; The production capacity of meltblown fabrics in the middle reaches grows slowly, and the number of manufacturers is small due to the small structural influence of the previous market, which is "the waist of gourd"; The leading enterprises producing melt-blown polypropylene in the upstream have expanded their production rapidly, which can basically meet the downstream demand for melt-blown materials. This is the "upper end of the gourd". Take Dawn Group as an example, the company has received orders for the next two months, and the daily production capacity of melt-blown materials has expanded from about 85 tons to about 200 tons now.
This embarrassing "thin waist" has become a "bottleneck" that restricts downstream production expansion.
The reporter’s investigation found that behind the bottleneck of melt-blown cloth production capacity is the difficulty and long time of production line expansion.
Yu Xiaoning and other people in the industry said that compared with the mask production line, the investment is small, the technical content is not high, the reproduction is fast, and the operation is easy. The production technology of meltblown cloth is high, and the quality of meltblown cloth directly determines the quality of masks. The production line investment of the cloth factory is tens of millions of yuan, and the equipment manufacturing and installation are much more complicated than the mask production device, and the requirements for the factory building are higher, and special training is needed for the staff.
At present, there are not many domestic manufacturers providing complete sets of production equipment and key components of meltblown fabrics, and the production of core components such as spinneret and spinneret die is still far from foreign manufacturers, and the delivery cycle and assembly time of imported equipment are relatively long. "The import delivery cycle of dies and spinnerets takes four to six months. Domestic molds can be delivered in two months, but this kind of mold with short delivery time can’t make high-end medical products. " Huang Wensheng said.
The procurement cycle of parts for several months limits the delivery capacity of meltblown fabric equipment, making it difficult to put it on the market overnight like a mask machine. It is understood that some enterprises that sell complete sets of melt-blown cloth production equipment are using inventory to quickly assemble new production lines. But the design, processing and debugging of a complete production line will take about two or three months.
A supplier of meltblown cloth production equipment in Zhejiang said that the production line of meltblown cloth was really introduced, and perhaps the peak demand brought by the epidemic had already passed. This kind of worry has prevented many investors from entering this field. The market scale of meltblown cloth is not large. Once the epidemic situation is over, the competitive pressure of meltblown cloth manufacturers will be very great.
Capacity to be tapped
Insiders pointed out that it is urgent to strengthen the overall planning of industrial chain, tap the potential of related enterprises and leading enterprises, and maximize the production capacity of meltblown fabrics.
Experts believe that in order to solve the problem that the supply of raw materials such as meltblown cloth in the mask industry chain is in short supply, the following measures can be taken to ensure the supply and price stability:
First, promote similar technology enterprises to switch production and supply mask materials.
According to the statistics of China Industrial Textile Industry Association, the production technology of China nonwovens industry is mainly spunbonded. In 2018, the output of spunbonded nonwovens was 2,971,200 tons, accounting for 50% of the total nonwoven production, which was mainly used in sanitary materials and other fields; However, the proportion of meltblown process is only 0.9%, and the output of meltblown nonwovens is 53,500 tons/year. These meltblown fabrics are not only used for masks, but also for environmental protection materials, clothing materials, battery diaphragm materials, wiping materials and so on.
Huang Wensheng said that enterprises that produce automotive sound insulation cotton, meltblown thermal insulation cotton, meltblown oil-absorbing cotton and other materials can switch to special filter materials for mask protection, and the annual production capacity of these enterprises is about 150,000 tons. It is understood that BYD, Changan Automobile, BAIC, SAIC and other automobile manufacturers have been taking advantage of the industrial chain to mobilize the supporting manufacturers of sound-absorbing cotton to transform the original production line of meltblown cloth and transform the production of special filter materials for masks.
Second, take the central enterprises as the leader and speed up the production line related to meltblown cloth.
The relevant person in charge of the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission said that the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission attaches great importance to the changes in the supply chain and industrial chain of domestic epidemic prevention materials and guides central enterprises to take the initiative to make up for shortcomings.
Because polypropylene, the raw material of melt-blown cloth, is taken from petroleum, petrochemical enterprises have advantages in producing melt-blown cloth. China Petrochemical Company has invested about 200 million yuan to build 10 melt-blown cloth production lines in Yanshan Petrochemical Company in Beijing and Yizheng Chemical Fiber Company in Jiangsu Province. After all the production, the daily output can reach 12 tons of N95 mask melt-blown cloth or 18 tons of medical flat mask melt-blown cloth, which can be processed into 18 million medical flat masks.
Third, strengthen government regulation and control to ensure the balance of upstream and downstream supply.
Lei Limin, vice president of China Textile Business Association, said that at present, the production situation of mask industry chain enterprises is complicated and information communication is not smooth, so it is difficult to know the real-time situation of the return to work rate and the newly put into production line. The industry believes that the mask industry chain is characterized by "marketization of upstream raw materials and administration of downstream masks", and the contradiction between market mechanism and plan management is constantly emerging. It is recommended to take administrative measures to properly intervene and straighten out the connection.
Yu Xiaoning said that in the face of the epidemic, the overall decision-making from the central government to the local government has solved many problems for the development of the industry. The next step is to strengthen the overall planning of the industrial chain, form an organic combination of government, industry associations and enterprises, and use big data to make comprehensive statistics on the number, distribution, production capacity and production capacity under construction of mask factories, cloth factories and raw material factories. In the extraordinary period, entrepreneurs should organize all kinds of production work well, at the same time, they should improve their consciousness from the overall height and cooperate with the government’s dispatch, which not only completes the epidemic prevention task, but also makes the market develop more orderly.