Looking back at the history of bicycles and motorcycles from the military, we can explore the wonderful past of "going to war alone"
Ride all the way to the battlefield
■ Zhang Naiqian
"Helicopter+motorcycle", can you imagine that this will become a "magic combination" on the modern battlefield? At the Dubai Air Show held not long ago, a UH-60 Black Hawk helicopter displayed by the United Arab Emirates carried an electric all-terrain motorcycle through a special side hitch. According to reports, the "combination" aims to use helicopters to bring the special warfare team into the mission area and complete the rapid assault by riding a motorcycle in the "last mile" of the battlefield.
Riding all the way to the battlefield was once a real historical picture. Whether bicycles or motorcycles, these "small two-wheeled land vehicles" were quickly put into the battlefield as soon as they came out, and a number of classic weapons were successively produced in magic change. Today, we can still see them in the armies of various countries.
In this issue of "Wide Angle of Weapons", let’s look back at the "Hundred Years’ Military History" of bicycles and motorcycles and explore the wonderful past of "going to war alone".

They have a "hundred years of military history"-
The battlefield iron horse emerged.
In the classic French comedy film "Escape from Danger" of World War II, the scene of German soldiers riding military motorcycles and chasing British pilots all the way made people sweat for the brave and tenacious pilots, and at the same time, they deeply realized the unique role of military motorcycles in mobile operations on the battlefield. In another World War II movie "War Day", the Danish army that resisted the German "Armored Corps" turned out to be an army equipped with bicycles.
Look at all kinds of bicycles and bike-sharing now shuttling through the streets. Have you ever thought that their "predecessors" used to be "iron horses in the battlefield"? Since ancient times, the pursuit of flexibility and mobility has been the eternal goal of the armies of various countries. Compared with horses, they need to be fed and carefully cared for. Bicycles are light and flexible to use, do not consume fuel, have low noise and are easy to hide. They can not only transport soldiers, but also cross rugged mountain roads. It’s no wonder that bicycles were quickly favored by armies of various countries after their birth.
On the battlefield of the Franco-Prussian War in 1870, the first military bicycle appeared. Prussian messengers rode bicycles to transmit information and orders on the battlefield, and the French army also sent bicycle squads to frequently penetrate the Prussian rear to spy on information. During the First World War, bicycles became one of the main equipment of the armies of the participating countries. France, Belgium and Britain each have more than 100,000 bicycle troops. Every light infantry battalion of the German Army has specially set up a bicycle company.
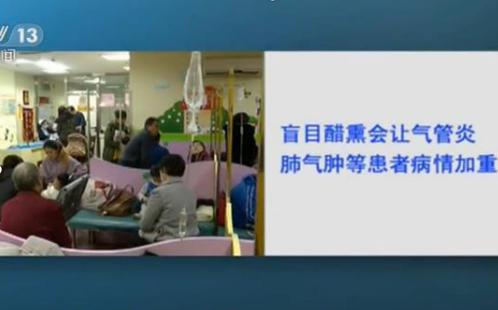
During the Second World War, the United States, the Soviet Union and Germany each had their own star "war horse". The American Harley-Davidson WLA motorcycle shines brilliantly on the battlefield, and the Soviet M-72 motorcycle is easy to produce and durable. The BMW R12, R35, R71 and R75 are all favored by the Germans. During the Iran-Iraq War, Iranian soldiers riding motorcycles quickly attacked the Iraqi army’s tank cluster, using rocket launchers, anti-tank grenades and burning grenades to storm the tank forces, and interpreted a unique war history of "motorcycles hitting tanks".
Today, bicycles and motorcycles are still indispensable and important "cars" for soldiers under complex terrain conditions. Regardless of the war in Afghanistan or Iraq, the U.S. military defines bicycles as special auxiliary equipment for Stryker armored vehicles and Hummer off-road vehicles. Once the vehicle breaks down, is destroyed or cannot pass through the terrain, the US military can take out its bicycle and ride all the way to the battlefield. In the open exercise screen of the Iranian Army in 2021, you can also see the scene of soldiers riding motorcycles to quickly launch a battlefield assault.
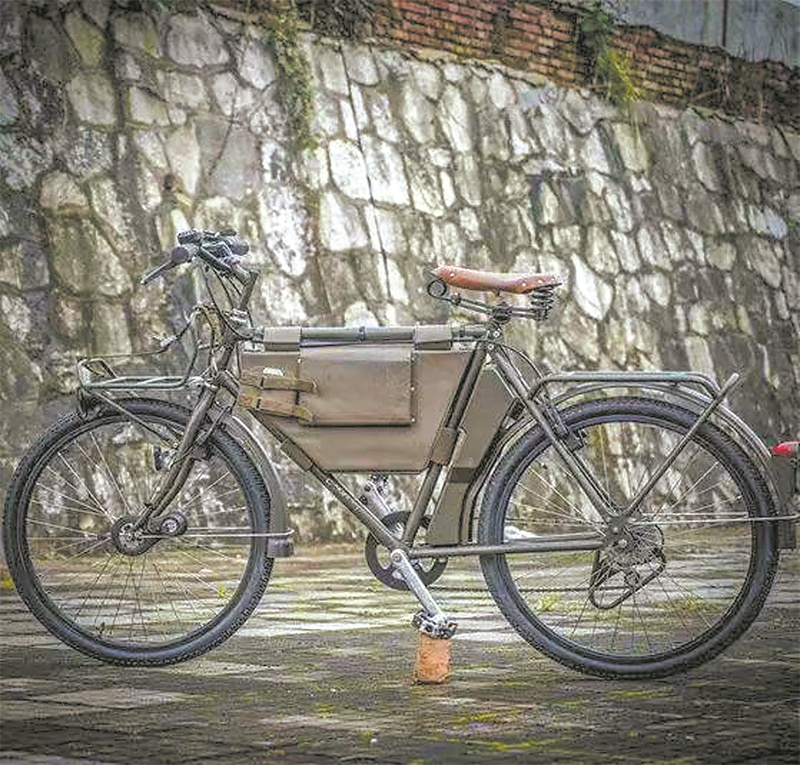

Swiss M93 military bicycle.
Bmw R75 motorcycle.
Not just a means of transportation—
Focus on operations and install "magic change"
At the China International Aviation and Aerospace Expo in 2018, China Aerospace Science and Technology Group displayed the "Cang Lang" missile launching system, which installed a multi-purpose missile launcher on an all-terrain motorcycle. The "infantry assault vehicle" equipped by the Nigerian Army can fully adapt to the local combat environment by installing protective shields and RPK series machine guns on motorcycles, and realize the integration of battlefield mobility and fire assault.
Since bicycles and motorcycles joined the army, they have been used for battlefield maneuvering, improving quick reaction ability, undertaking reconnaissance, vigilance and transportation tasks, and also quickly entered the battlefield "magic change" era with various weapons. British-designed BSA military bicycle has a rifle support clip installed at the seat strut for fixing guns; Italians who dare to "try early" put Maxim’s heavy machine guns on tandem two-seater bicycles; Germany also installed anti-tank weapons and light mortars on TR-FA bicycles. These "machine-gun chariots" react quickly, and the bomb load is not small in the case of multi-vehicle cooperation. They are strange weapons with both offensive and defensive functions on the battlefield.
Compared with bicycles, motorcycles are also a good platform for carrying weapons. During World War II, the Germans equipped heavy-duty sidecar motorcycles with machine guns, carrying several boxes of machine gun bullets and sometimes a light mortar. During the Battle of Berlin in 1945, the Germans used armed bicycles and motorcycles to infiltrate and sneak attack Soviet armored forces and destroyed a number of Soviet tanks.
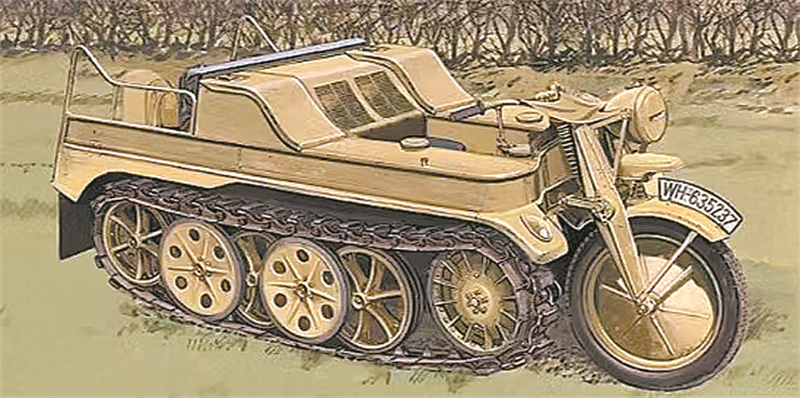
Another one written in the history of weapons is the German Sdkfz.2 semi-crawler motorcycle. The first half of this motorcycle is no different from ordinary motorcycles, but the second half uses staggered load wheels and crawler-type walking devices, so it is called "Centaur". In 1941, this type of motorcycle was officially put into operation on the eastern front by the German army in the Barbarosa operation, showing its strong passing ability on the muddy road conditions on the battlefield. In fact, whether it is transporting ammunition, pulling artillery, or pulling a few heavily armed soldiers to support the front line, its battlefield performance is remarkable, and the German Air Force even uses it to tow aircraft, which is called the "all-purpose oil" equipment of the Germans on the battlefield.
Will motorcycle.
German semi-crawler motorcycle.
Get through the "last mile" of the battlefield-
The wheels are rolling and the stage is vast.
With the smoke of World War II dispersed, mechanization and informatization have become the main theme of military development in various countries, and a large number of mechanized equipment have been installed one after another. As "veterans" in the military, bicycles and motorcycles seem to be slowly retiring. In fact, as a portable vehicle that can get through the "last mile" of the battlefield, cycling vehicles still have a broad stage in the modern battlefield.
Rapid force delivery should not be underestimated. As the most "bicycle-loving" army, the Swiss bicycle force was not abolished until the beginning of this century. When you open the map, you can find that Switzerland, which has many mountains and lakes, is a "paradise" for cycling troops. They can cross most mountain roads without fuel and fight in various complex terrain conditions. For this reason, even though the special bicycle troops were cancelled, Switzerland still has not given up military bicycles. Besides exercising physical fitness and adapting to the unique mountain environment, it is also specially used for special forces. Compared with bicycles, armies all over the world still keep a certain number of military motorcycles. Germany’s latest "BMW" F850 GS military motorcycle is a cross-country motorcycle specially used for fast maneuvering.
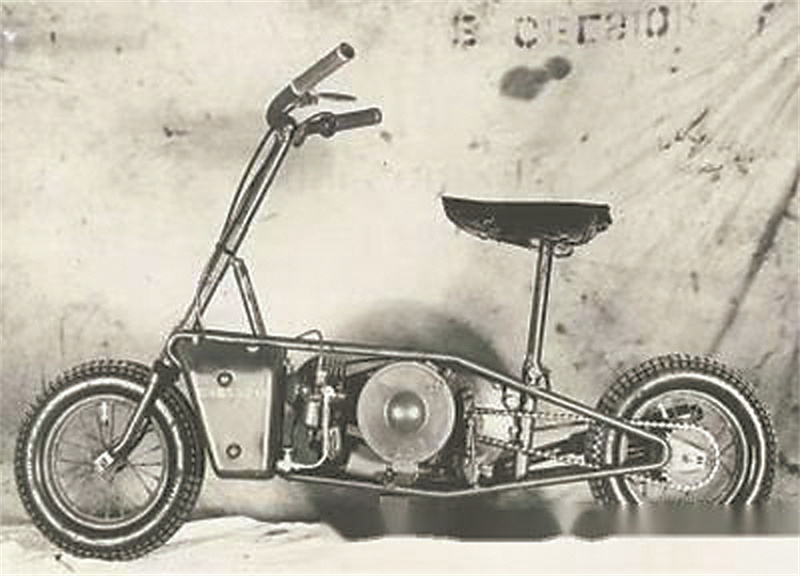
Folding portability is favored by officers and men. In addition to constantly improving the attack capability, folding and portability has also become the direction of bicycle and motorcycle modification. During World War II, British and German airborne troops were equipped with folding paratroopers’ bicycles. Britain has specially designed Will folding motorcycles for British special operations forces and airborne troops. After the motorcycle is folded and airdropped by a special umbrella bag, it can be unfolded and set off within 10 seconds. In the 1980s, multifunctional mountain bikes and foldable paratroopers developed by the US Department of Defense entered the US military service. The "Paratrooper" folding bicycle weighs 14 kilograms, can carry 150 kilograms, and the length and width of the body are not more than 90 centimeters. The bicycle can be folded or unfolded within 30 seconds. Because it is light and small, the "paratrooper" folding bicycle can be tied to the outside of tanks and armored vehicles, or hung on the paratroopers’ chest to skydive together, giving paratroopers flexible and fast mobility.
Electric silent or become the trend of the times. The electric car has good mute performance, and the sound it makes is even smaller than the voice of people. It can be used for special forces to quickly pass through rugged terrain and launch battlefield raids quietly. The "EZ Rider" electric vehicle being tested by the US Special Forces and the Israel Defense Forces can haul 250 kilograms of materials and travel nearly 40 kilometers on a single charge, which is suitable for special forces. The "Golan" electric off-road vehicle developed by Russia has a top speed of 110 kilometers per hour and a cruising range of 370 kilometers with additional batteries. Russia also specially installed AK-74 rifles, RPG rocket launchers and Grenade launchers for the "Golan" electric off-road vehicle, in order to play an important role in future special forces’ ambush and reconnaissance operations.
Layout design: Xie An
E-mail for this edition: jfjbbqdg@163.com